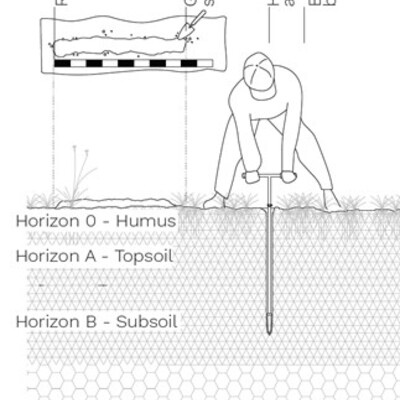
Fieldwork: soil sampling
Soil sampling is one of the methods used to document and translate characteristics of the soils. By drilling or digging into the soil, one can get a picture of the interior of the soil and its horizons to undertake various tests to determine its characteristics. So analyzing and monitoring chemical, physical and biological parameters of soil health can often be accomplished with just a shovel and some thoughtful observation.
The soil tests used in the test plots in Senan are specifically designed for practitioners who want to sample soil directly in the field with limited time and equipment. Consequently, the tests are qualitative in nature and do not allow for quantitative conclusions. They include the following:
- Soil profile: A soil profile is a vertical cross-section of the soil. It usually consists of layers running parallel to the surface, called soil horizons.
- Soil color: Soil color is the color of the soil, which is mainly influenced by the three pigments black (from organic material), red (from iron and aluminum oxides), and white (from silicates and salts).
- Soil texture: Soil texture refers to the proportion of sand, silt and clay particles that make up the mineral fraction of the soil. as opposed to the organic parts of the soil (e.g. humus or roots).
- Soil pH: Soil pH is the measure of the acidity (sourness) or alkalinity (sweetness) of a soil. A pH value is effectively a measure of hydrogen ion concentration (H+).
- Lime test: The lime test is an indicator for carbonates and shows the lime content of a soil sample. The application of a few drops of hydrochloric acid (HCl) to a soil sample containing carbonates results in the evolution of CO2 gas, which forms bubbles and causes the soil to effervesce.
- Hydrogen peroxide test: The hydrogen peroxide test is an indicator for soil organic carbon. Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) reacts with the organic carbon in the soil and forms CO2 bubbles and causes the soil to effervesce.
- Water infiltration: Water infiltration is the process by which water infiltrates through the soil surface into the soil.